When I was assembling my first gaming PC by selecting the ideal motherboard form-factor between Mini-ITX, Micro-ATX, and ATX. I selected Micro-ATX because it was half the size of ATX but still provided me with incredible potential for future expansion into my mid-tower case. Knowing these form factors was the key to making all the difference in achieving the build that I needed.
Mini-ITX vs Micro-ATX vs ATX – It is very important to know your PC requirements and understand what you need in order to decide between these form factors. Mini-ITX is ideal for small form factor builds, offering compactness and portability. Micro-ATX strikes a balance between price and space, making it a versatile option. ATX, on the other hand, provides more space for components, making it suitable for high-performance setups. Understanding these form factors is crucial to ensure proper integration and optimal functionality for your system.
Stay tuned with us as we dive deep into the world of PC builds, exploring Mini-ITX vs Micro-ATX vs ATX: What Size of a Mobile Device Do You Need? Read on and find out the ideal pick for your configuration in our comprehensive buying guide below!
Table of Contents
What Are Motherboard Form Factors?
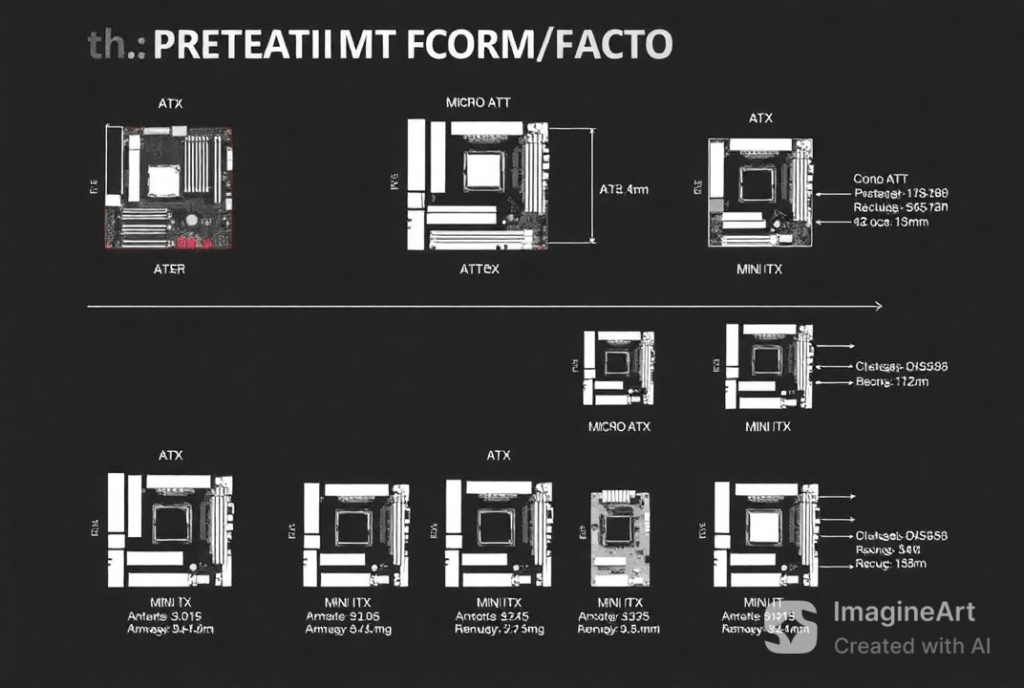
A Motherboard form factors refer to the dimensions, form and placement layout of the motherboard. They indicate which cases such specifications apply, how many components they are limited to, and their capacity. Over the years, form factors have changed, allowing a variety of form factors from the small form factor to ambitious and highly performant gaming machines.
The idea that each form factor can be advantageous and disadvantageous in certain goals should guide the choice of each form factor. The primary motherboard form factors we’ll focus on are:
- Mini-ITX: In particular, it is rather customary for compact and small form-factor (SFF) computer systems.
- Micro-ATX: A functional and cheap type of furnishing.
- ATX: The gaming, high-performance or standard PC size.
Size Comparison: Dimensions and Their Implications
The size of a motherboard plays a key role in the compatibility of a given motherboard to support most PC cases and the number and availability of ports and slots as well as the overall performance of the system. Below is a breakdown of the sizes:
Mini-ITX
- Dimensions: 6.7” x 6.7”
- Key Features:Smallest form factor.It is commonly incorporated with one PCIe slot and two RAM slots.Perfect for small cases and even most mobility desks or transportation compartments.
- Use Case: Great for compact solutions or home stations and gaming PC.
Micro-ATX (mATX)
- Dimensions: 9.6” x 9.6”
- Key Features:It is larger than the Mini-ITX with more opportunities for expansion than Mini-ITX.Usually comes with upto four RAM slots and several PCIe lanes.Good for low-cost systems and comes in different form factors.
- Use Case: Common for low-cost gaming or for building a general purpose PC.
ATX
- Dimensions: 12” x 9.6”
- Key Features:A standard size of the body is provided to accommodate a sufficient number of ports and slots.Yes it supports multi GPU system and overclocking, Also high RAM capacity is also supported.Ideal for those configurations optimized for performance or appearance.
- Use Case: Perfect for TCP/IP,-mortgage-banking, media, fans, power tools, graphic art and high-performance gaming computers.
Features & Capabilities
Understanding the distinct features and capabilities of each form factor will help you decide which one aligns with your needs.
Mini-ITX
Advantages:
- Small footprint for compact cases.
- Simplifies cable management due to fewer components.
Limitations:
- Limited expandability (single PCIe slot).
- Higher heat concentration due to compact design.
- Fewer options for overclocking and RAM.
Micro-ATX
Advantages:
- Balance between size and expandability.
- Budget-friendly without sacrificing key features.
Limitations:
- Less appealing aesthetics compared to larger boards.
- Fewer PCIe slots than ATX boards.
ATX
Advantages:
- More PCIe lanes and RAM slots.
- Better support for overclocking and advanced cooling systems.
- Aesthetically pleasing with room for RGB and cable routing.
Limitations:
- Larger cases required.
- Higher cost compared to smaller form factors.
Use Cases and Suitability
To determine the best form factor for your PC, consider your intended use case:
Budget Builds
- Best Option: Micro-ATX
- Reason: Cost-effective without sacrificing essential features.Compatible with a wide range of affordable cases.
Gaming PCs
- Best Option: ATX or Mini-ITX
- Reason: ATX supports multi-GPU setups and overclocking for high-end gaming rigs.Mini-ITX is suitable for compact gaming systems with modern GPUs.
Small Form-Factor PCs
- Best Option: Mini-ITX
- Reason: Ideal for users prioritizing portability or minimalist design.
Content Creation and Workstations
- Best Option: ATX
- Reason: Ample expandability for GPUs, storage, and memory.
Read More : Motherboards for AI Workstations: AMD vs Intel in 2025
Pros and Cons of Each Form Factor
| Form Factor | Pros | Cons |
| Mini-ITX | Compact, Portable | Limited slots, Higher cost |
| Micro-ATX | Affordable, Versatile | Aesthetic limitations |
| ATX | High performance, Expandable | Larger size, Expensive |
Key Factors to Consider Before Buying
- Case Compatibility: Ensure your case supports the chosen motherboard size.
- Cooling Requirements: Larger boards typically support advanced cooling solutions.
- Expandability: Consider PCIe slots, RAM slots, and storage needs.
- Aesthetics: Match the motherboard size with your design preferences.
FAQs
1. Can I use an ATX motherboard in a Micro-ATX case?
No, ATX motherboards are larger and will not fit in smaller Micro-ATX cases.
2. What’s the best form factor for gaming?
ATX is the best for high-performance gaming, while Mini-ITX works well for portable builds.
3. Is Mini-ITX more expensive than Micro-ATX?
Yes, Mini-ITX motherboards are often pricier due to their compact design.
Conclusion
Choosing the right motherboard form factor depends on your priorities. Whether you’re building a high-end gaming rig, a budget-friendly PC, or a portable system, aligning your needs with the capabilities of Mini-ITX, Micro-ATX, or ATX will ensure a successful build. For more tailored advice, check out our in-depth guides on motherboards for gaming and small form-factor cases.
